The Affordable Care Act has made it more accessible for millions of Americans to afford health coverage. It also shields consumers from insurers’ tactics that might hike up costs or restrict care.
But the ACA’s numerous spending and offset provisions must be fixed so people can continue to reap these benefits.
Cost-sharing reductions
The Affordable Care Act/Obamacare makes health insurance more accessible by reducing deductibles, copayments and coinsurance that people pay when using covered healthcare services. This makes it easier for those with lower incomes to purchase affordable plans.
Cost-sharing reductions (CSR) are available to low-income individuals and families with household incomes between 100% and 250% of the federal poverty level. They reduce deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance that Marketplace enrollees pay when using covered health care services.
Individuals and families who purchase a silver plan through the Marketplace will automatically be provided with a version of the plan with reduced out-of-pocket costs, such as a lower deductible, out-of-pocket maximum, and copayments.
Costs will differ between individuals and plans. While these prices cannot be guaranteed by the federal government, they do help make Silver plans more accessible for many consumers.
Premium tax credits
Under the Affordable Care Act, premium tax credits help lower health insurance costs for consumers. These credits are distributed on a sliding scale to individuals and families who purchase qualified health plans from either state or federal Marketplaces.
To receive the credit, you must file an ACA-specific income report. This report determines how much of a tax credit you are eligible for; it can be paid out in advance throughout the year or as one lump sum at yearend.
Under the Affordable Care Act, individuals whose incomes fall between 100 percent and 400% of the federal poverty level can take advantage of a premium tax credit to reduce their health insurance costs. This has made healthcare more accessible and affordable for millions across America.
Expansion of Medicaid
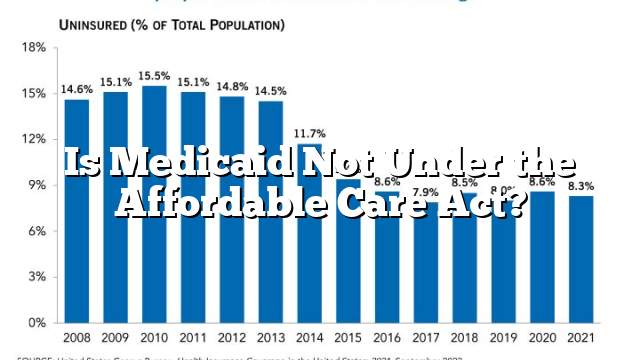
Under the Affordable Care Act, Medicaid eligibility was extended to non-disabled adults whose household incomes did not exceed 138% of the federal poverty level (in 2013: about $18,000 for an individual, $24,000 couple and $37,000 family of four). As a result, millions more people will gain access to health insurance.
In addition to providing health coverage, the Affordable Care Act expanded Medicaid access to a variety of essential or front-line workers such as transportation, waste management and child care. Now, nearly 5 million workers in these industries are covered by Medicaid coverage.
Evidence indicates that expanding Medicaid access increases access to health care, reduces out-of-pocket expenses, and improves outcomes for low-income people. While different studies use different data sets, research designs, and outcome measures, these results generally support the idea that expanding Medicaid improves health and well-being. It is essential to evaluate these changes holistically in order to make sure all benefits of the law are being realized.
Health insurance marketplaces
Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), you can access affordable health insurance through a marketplace run either by state governments or the federal government.
Marketplaces enable consumers to compare health plans, determine if they qualify for subsidies, and pick the plan best suited to their needs and budget. Furthermore, they offer consumer protections against discrimination based on pre-existing conditions and gender.
Marketplaces enable people to compare plans based on price, quality and networks. In addition to the standard bronze, silver, gold and platinum level plans, some marketplaces may provide catastrophic options as well.
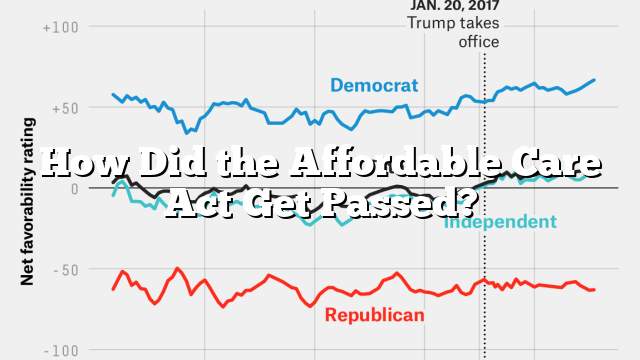
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has enabled millions of Americans to secure affordable health insurance. Unfortunately, the law has been met with some controversy, such as court challenges and delays in key provisions.